Research and development
21. May 2025
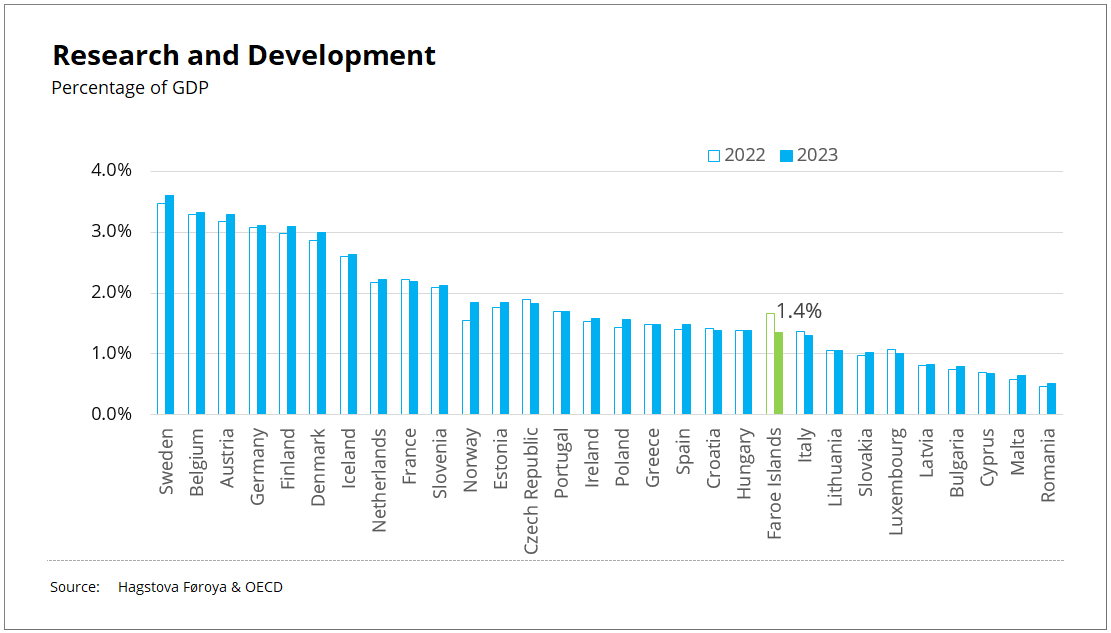
Faroese R&D expenditure relative to GDP at 1.4%

Please note that on August 7th 2025 the following edits were made:
In the original article from May 21st 2025 under the headline, “Lowest investments in R&D among Nordic countries” a few statistics were regrettably wrongly reported. Originally the stat for Norway was reported as 1,6% (which has been corrected to 1,9%), for Denmark 2,9% (corrected to 3,0%), for Finland 3,0% (corrected to 3,1%), and for Sweden 3,5% (corrected to 3,6%). The text is unchanged from the original piece, and the conclusion is therefore the same, “In 2023, the Faroe Islands' expenditure on R&D as a percentage of GDP was the lowest of the Nordic countries. This was also observed in 2022.”
Statistics Faroe Islands announces, for the second time, statistics on research and experimental development (R&D) in collaboration with Research Council Faroe Islands. The statistics follow international guidelines making them internationally comparable. Minor retroactive adjustments have been made to the 2022 statistics.
1.4% of GDP
The key figure used in measuring a country’s R&D activity is the gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD). In the Faroe Islands, DKK 367 million were spent on R&D in 2023, equivalent to 1.4% of its GDP.
In 2022, R&D expenditure was 1.7% of GDP. The 2023 expenditure therefore represents a 0.3 percentage points decrease or DKK 52 million. The GDP has grown by 6.7% in current prices during the same period, also affecting the trend.
Annual fluctuations in the Faroese R&D expenditure is to be expected, as it’s driven and influenced by relatively few institutions and companies.
[px-graph-6]
Lowest investments in R&D among Nordic countries
In 2023, the Faroe Islands' expenditure on R&D as a percentage of GDP was the lowest of the Nordic countries. This was also observed in 2022.
In 2023 Norway allocated 1,9% of its GDP to R&D, Iceland 2,6%, Denmark 3,0%, Finland 3,1% and Sweden committed 3,6%.
Across all Nordic countries, R&D expenditure as a percentage of GDP decreased slightly in 2023 compared to 2022.
Private sector accounts for two-thirds of R&D expenditure
In 2023, private enterprises in the Faroe Islands reduced their R&D spending by 20.9%. Conversely, public institutions and higher education establishments increased their R&D expenditure by a combined total of 13%.
Despite the decline, the private sector remains the dominant contributor to R&D funding, accounting for over two-thirds of the total expenditure. Specifically, businesses invested 0.9% of GDP into R&D, while the public sector and higher education institutions contributed 0.3% and 0.2% of GDP, respectively.
Tertiary industries now account for the largest share of R&D expenditure
In 2023, companies and institutions in the tertiary sector accounted for 58% of the total R&D expenditure in the Faroe Islands. The primary sector contributed 33%, and the secondary 9%. This marks a shift from 2022, when the primary sector represented more than half of GERD.
The tertiary sector includes retailing and wholesale, hotel and restaurants, transport and storage, information and communication, bank and insurance, real estate and accommodation, leasing and renting, public administration, education, health services, social systems and other services.
The primary sector includes fishery, sea farming and other primary sectors, while the secondary sector includes food production, other production, water supply and construction.
[px-graph-3]
252 full-time equivalents in R&D
In 2023, a total of 252 full-time equivalents (FTEs) were registered in the field of R&D. The gender distribution among researchers was 57% men and 43% women.
While men occupy 80% of technical positions, the gender distribution is even among scientific assistants.
[px-graph-4]
Definitions
Research and development
Research and experimental development encompasses creative and systematic work undertaken to expand the frontiers of knowledge and develop new applications for existing knowledge.
All five main criteria below must be met for an activity to be considered research and experimental development:
- Novel: must aim to create new knowledge.
- Creative: must be based on new concepts, proposals or scientific hypotheses. Regular procedures such as updates and software maintenance are thus not regarded as R&D activities.
- Uncertain: at the start of an R&D project, outcomes and costs cannot be precisely determined beforehand.
- Systematic: R&D is conducted in a planned way, with records kept of both the process followed and the outcome. The purpose and the sources of funding for the R&D performed must be identified.
- Reproducible: an R&D project must be thoroughly documented to facilitate both internal and external use. This allows other researchers to reproduce the results and build upon them in their own R&D work.
GERD is the gross domestic expenditure on R&D. GERD – particluarly GERD as a percentage of GDP – is the main indicator for international comparisons of R&D.
GERD covers the total domestic expenditures on research and development incurred during a specific period, i.e. all expenditures on R&D conducted in the four main sectors, including work involving funding from abroad. However, GERD does not cover R&D conducted abroad, even though this work may be carried out by Faroese researchers or with Faroese funding.
Only R&D conducted intramurally, i.e. within the same unit, is counted towards GERD. Funding for extramural R&D is not included. This is done to avoid double counting.
% of GDP
Expenditures on R&D as a percentage of GDP in current prices.
GDP is a measure of the total value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a specific period. These goods and services are the result of the combined efforts of various factors, including materials, labour and production tools.
GDP in current prices means that the GDP is measured using the prices that are in effect during the year measured.