Research and development
28. Jun 2024
Faroese R&D expenditure relative to GDP at 1.5%

Statistics Faroe Islands has published its first figures on research and experimental development since 2003, in collaboration with the Faroese Research Council. These statistics follow international standards, allowing for global comparisons.
GERD data will be updated annually, providing an ongoing resource for tracking R&D investment in the Faroes.
1.5% of GDP
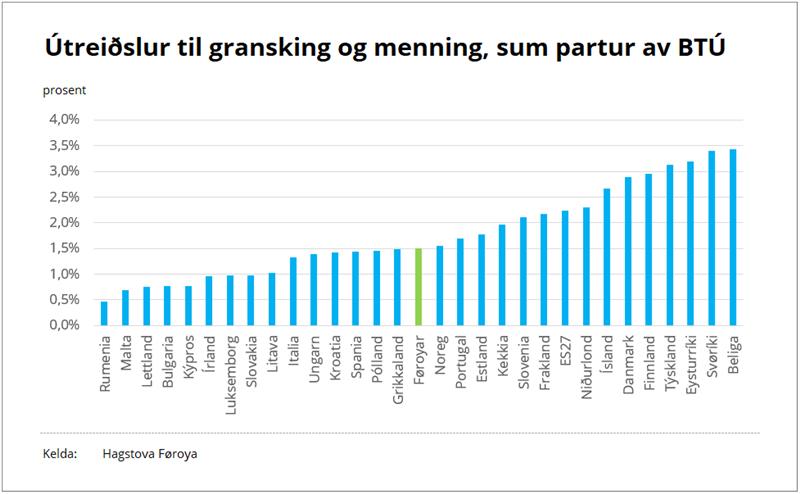
The key figure used in measuring a country’s R&D activity is the gross domestic expenditure on R&D (GERD). In 2022, the Faroes spent DKK 376 million on R&D, equivalent to 1.5% of its GDP.
In 2003, the last time GERD data was compiled in the Faroes, this figure was 0.9%. It should be noted that the Faroese GDP has increased significantly since 2003.
The Faroes have the lowest GERD figure in the Nordic region. Norway has a GERD of 1.6%, Iceland 2.7%, Denmark 2.9%, Finland 3.0% and Sweden 3.4%.
Private sector drives GERD growth
Business enterprises account for more than two-thirds of expenditures for R&D in the Faroes, representing 1.1% of GDP. The public sector and higher education contribute 0.3% and 0.1% of GDP, respectively.
This marks a significant shift from 2003, when the total GERD was at 0.9% of GDP: business enterprises accounted for 0.2% of GDP and the public sector and higher education represented 0.7%.
[px-graph-1]
Primary industries lead R&D
Primary industries are the source of more than half of Faroese R&D, with aquaculture leading the way.
Secondary and tertiary industries represent 7% and 35%, respectively.
[px-graph-3]
276 full-time equivalents in R&D
In 2022, a total of 276 full-time equivalents (FTEs) were registered in R&D, 153 men and 123 women. There is a fairly even split between the two sexes in research positions, although there are more male technicians and scientific assistants.
In 2003, there were 131 FTEs in R&D.
[px-graph-4]
Definitions
Research and development
Research and experimental development encompasses creative and systematic work undertaken to expand the frontiers of knowledge and develop new applications for existing knowledge.
All five main criteria below must be met for an activity to be considered research and experimental development:
- Novel: must aim to create new knowledge.
- Creative: must be based on new concepts, proposals or scientific hypotheses. Regular procedures such as updates and software maintenance are thus not regarded as R&D activities.
- Uncertain: at the start of an R&D project, outcomes and costs cannot be precisely determined beforehand.
- Systematic: R&D is conducted in a planned way, with records kept of both the process followed and the outcome. The purpose and the sources of funding for the R&D performed must be identified.
- Reproducible: an R&D project must be thoroughly documented to facilitate both internal and external use. This allows other researchers to reproduce the results and build upon them in their own R&D work.
GERD is the gross domestic expenditure on R&D. GERD – particluarly GERD as a percentage of GDP – is the main indicator for international comparisons of R&D.
GERD covers the total domestic expenditures on research and development incurred during a specific period, i.e. all expenditures on R&D conducted in the four main sectors, including work involving funding from abroad. However, GERD does not cover R&D conducted abroad, even though this work may be carried out by Faroese researchers or with Faroese funding.
Only R&D conducted intramurally, i.e. within the same unit, is counted towards GERD. Funding for extramural R&D is not included. This is done to avoid double counting.
% of GDP
Expenditures on R&D as a percentage of GDP in current prices.
GDP is a measure of the total value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a specific period. These goods and services are the result of the combined efforts of various factors, including materials, labour and production tools.
GDP in current prices means that the GDP is measured using the prices that are in effect during the year measured.